Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are on the rise due to our tech-driven world and repetitive tasks. Manual laborers, athletes, and those with sedentary lifestyles are at risk. Key triggers include prolonged typing without breaks, intense grip tools, poor posture, lack of stretching, and improper ergonomics. Recognizing these factors is vital for prevention and minimizing RSI occurrence. Symptoms include stiffness, numbness, and pain radiating through the upper limbs. Chiropractic treatment coupled with functional rehabilitation exercises offers a holistic approach to management, expediting sports injury recovery and enhancing overall joint health.
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is a growing concern in today’s fast-paced, tech-driven world. This article delves into the intricate web of risk factors contributing to RSI, offering valuable insights for prevention and mitigation. We explore common triggers such as overuse and repetitive tasks, poor posture and ergonomics, and individual susceptibility. Understanding the impact on specific body parts like wrists, shoulders, and neck is crucial. Additionally, we provide actionable strategies focusing on workstation setup, breaks, exercises, and stretches to combat RSI effectively.
Identifying Common Risk Factors

Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are a growing concern in modern society due to our increasing reliance on technology and repetitive tasks. Identifying common risk factors is essential in understanding and preventing these injuries, especially among individuals engaged in manual labor or sports. Some key risk factors include prolonged periods of repetitive motion, such as typing on a keyboard for extended hours without breaks, or the frequent use of tools that require intense grip and strain.
These activities place excessive stress on muscles, tendons, and nerves, leading to inflammation and potential damage over time. Additionally, poor posture, inadequate stretching routines, and lack of proper ergonomic setup can exacerbate these issues. Post-injury care becomes more challenging without awareness of these risk factors, as they can slow down the muscle recovery process in sports injury recovery scenarios. Recognizing these triggers is a proactive step towards minimizing the occurrence of RSIs and promoting better overall health.
– Overuse and Repetitive Tasks

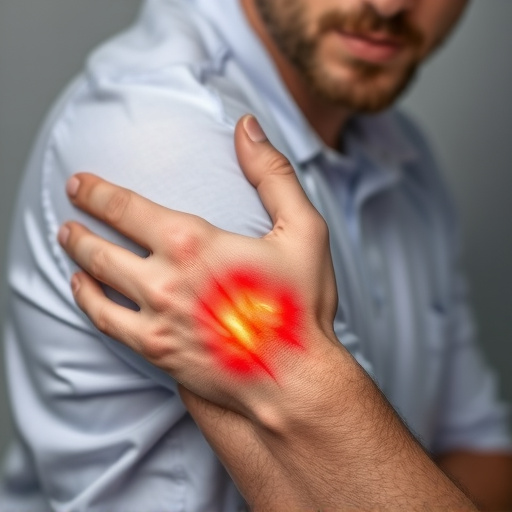
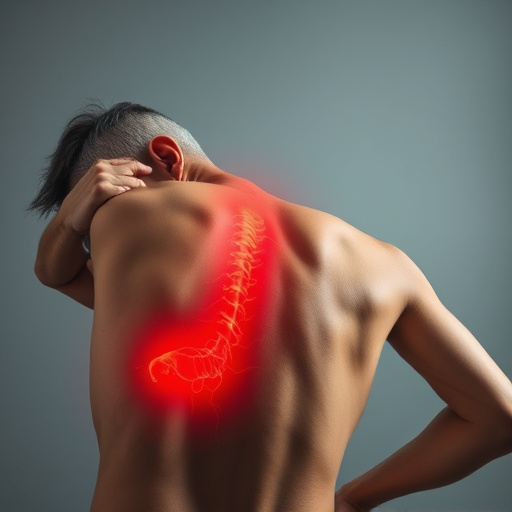
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is often caused by prolonged exposure to activities that involve repetitive movements or sustained positions. This includes tasks such as typing, clicking a mouse, or any other activity where the same muscle groups are repeatedly stressed over an extended period. Overuse of these muscles can lead to inflammation and subsequent joint pain relief issues, affecting not just the hands and wrists but also shoulders, elbows, and even arms.
These repetitive tasks contribute to a range of RSI symptoms, including stiffness, numbness, and pain that may spread throughout the upper limbs. In sports or active individuals, such overuse injuries are common, especially during training or competitive events where athletes might push themselves to perform the same movements repeatedly. Fortunately, mobility improvement techniques can help manage and alleviate these symptoms, aiding in faster sports injury recovery.
– Poor Posture and Ergonomics

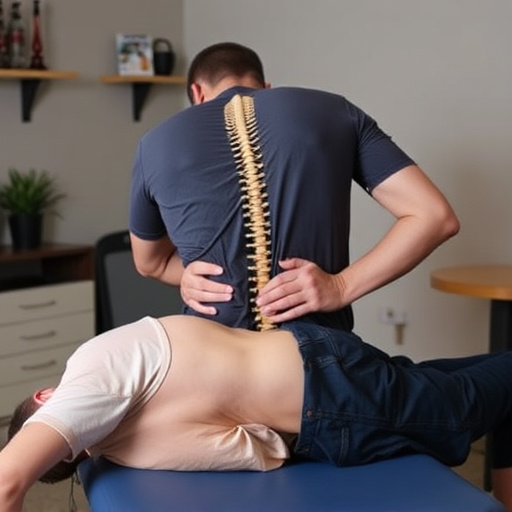
Poor posture and ergonomics are significant risk factors for repetitive strain injury (RSI), a common condition affecting various parts of the body due to repeated or prolonged activities. Many individuals, especially those with sedentary jobs or who spend long hours using computers, may not realize their postural habits contribute to RSI development. Inadequate workstation setup, such as incorrect chair height, keyboard placement, or monitor position, can lead to muscles and joints being held in abnormal positions for extended periods. This puts excessive strain on specific areas, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential nerve compression over time.
Chiropractic treatment, along with functional rehabilitation exercises, can help address these issues. Chiropractors can assess posture and provide guidance on ergonomic improvements at work and home. They may also employ manual therapy techniques to reduce muscle tension and improve joint mobility. Additionally, functional rehab focuses on strengthening and stretching specific muscles to support the body’s natural alignment, thereby reducing the risk of RSI and promoting overall joint health and pain relief.
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a growing concern in today’s workspace, where prolonged periods of static tasks and poor posture are common. By identifying risk factors such as overuse of specific muscles and inadequate ergonomics, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent RSI. Adopting better habits, including regular breaks and ergonomic adjustments, can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this debilitating condition, ensuring a healthier and more productive future for all.