Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is a spectrum of conditions caused by repetitive tasks or awkward postures, affecting muscles, tendons, and nerves. Early indicators like tingling fingers should be addressed seriously to prevent chronic pain and disability. Ergonomic workspaces, featuring adjustable desks, ergonomic chairs, and breaks, along with non-invasive treatments like functional rehabilitation, significantly reduce RSI risk. Healthy work habits, including proper posture, regular stretching, and correct mouse/keyboard technique, also minimize the risk of RSI. Post-injury care should include targeted exercises for recovery to foster an injury-free environment.
Preventing a repetitive strain injury (RSI) is crucial for maintaining productivity and overall well-being in the workplace. This article delves into the root causes of RSI, offering insights on recognizing symptoms early. We explore ergonomic solutions for creating optimized workspaces that minimize risks. Additionally, practical strategies for fostering healthy habits are provided to ensure comfort and prevent long-term discomfort associated with repetitive tasks.
- Understanding Repetitive Strain Injury: Causes and Symptoms
- Ergonomic Workspaces: Designing for Prevention
- Strategies for Healthy Habits at Work
Understanding Repetitive Strain Injury: Causes and Symptoms
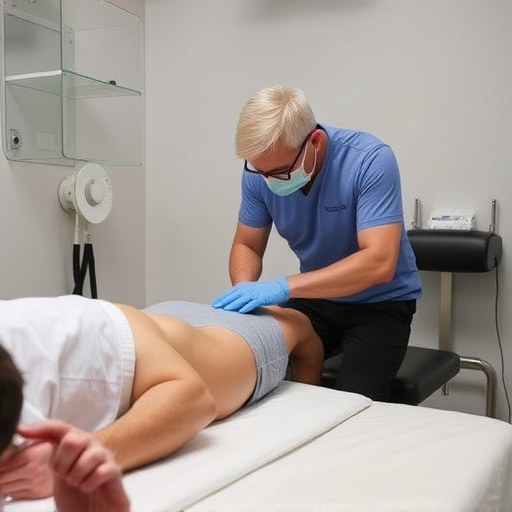
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is a collective term for a range of conditions affecting muscles, tendons, and nerves due to repetitive tasks or sustained awkward postures. It’s crucial to understand that RSI isn’t just about muscle aches; it can lead to severe pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected areas. For example, sciatica relief might be a concern for those with RSI as compression of the sciatic nerve is a common symptom.
Causes are varied, from repetitive motions like typing or clicking a mouse to prolonged periods in one position. Symptoms can include pain, tenderness, stiffness, and decreased grip strength. Early signs may be subtle, like tingling fingers after a day at the desk, but if left unaddressed, they can escalate into chronic pain and disability. Seeking wellness care and considering functional rehabilitation strategies are important steps to prevent RSI from escalating, ensuring your long-term comfort and productivity at work.
Ergonomic Workspaces: Designing for Prevention
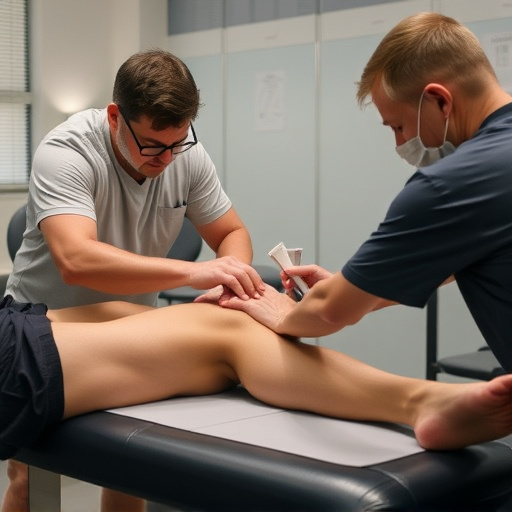
Ergonomic workspaces play a pivotal role in preventing repetitive strain injuries (RSI), which are common among those who perform repetitive tasks for extended periods. Designing an office or workstation with ergonomics in mind can significantly reduce the risk of developing RSI. This involves ensuring proper posture support, reducing static positions, and minimizing strain on the body’s muscles and joints.
Implementing ergonomic features such as adjustable desks, ergonomic chairs, and wrist rests can create a more comfortable and supportive environment. Additionally, regular breaks to stretch and move around, along with proper lifting techniques and organized workspaces, contribute to long-term wellness. Even non-invasive treatment methods like functional rehabilitation and physical therapy can be integrated into the workplace to offer immediate relief and promote better work habits for an injury-free environment.
Strategies for Healthy Habits at Work
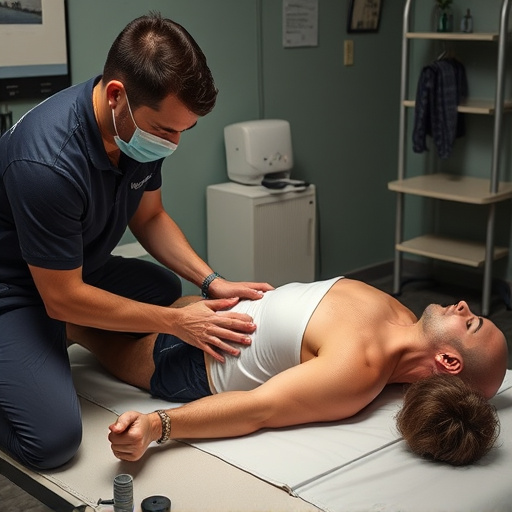
Developing healthy habits at work is a proactive approach to preventing repetitive strain injuries (RSI). One of the key strategies is maintaining proper posture while sitting or standing. Ergonomic furniture, such as adjustable desks and chairs, can help support your body’s natural alignment, reducing muscle tension and joint pain relief over time. Regular breaks are also essential; every hour, take a short break to stretch, walk around, and give your eyes a rest if you work on a computer. This helps prevent muscle stiffness and promotes overall well-being.
Additionally, practicing good mouse and keyboard technique can significantly reduce the risk of RSI. Keep your wrist straight and neutral while typing, with minimal bend or tilt. Use a wrist support to maintain this position, especially if you spend long hours at a desk. After an injury, post-injury care should include specific exercises for muscle recovery, focusing on strengthening and stretching exercises tailored to the affected area. By incorporating these healthy habits into your workday, you can create a more ergonomic environment and significantly lower your chances of experiencing or exacerbating repetitive strain injuries.
Preventing a repetitive strain injury (RSI) at work is achievable through understanding its causes, adopting ergonomic practices, and cultivating healthy habits. By designing workspaces that accommodate proper posture and reducing repetitive tasks, you minimize the risk of RSI. Remember to take regular breaks, maintain good posture, and vary your activities throughout the day. These strategies, combined with awareness of symptoms, can help foster a comfortable and productive work environment, ensuring your well-being in the long run.