Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) causes physical and emotional distress, impacting daily activities and mental health. Psychological support alongside physical therapy is essential for recovery. Mindfulness, low-impact exercises, tailored therapy, and support groups aid in managing RSI's effects on mental wellness.
Mental health challenges and repetitive strain injury (RSI) are closely intertwined. This article delves into the complexities of RSI, exploring its psychological impact on individuals struggling with chronic pain and discomfort. We’ll discuss common causes of this occupational hazard and provide effective coping strategies to enhance mental wellness. By understanding RSI’s mental health implications, we can better navigate and manage this debilitating condition.
- Understanding Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) Causes
- Psychological Impact of Chronic Pain and Discomfort
- Effective Coping Strategies for Mental Wellness
Understanding Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) Causes
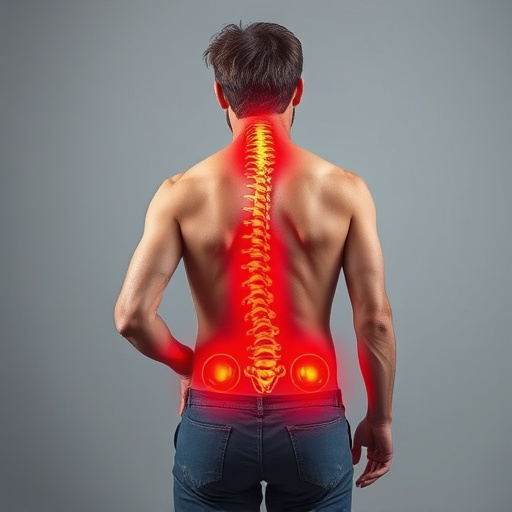
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) arises from repetitive or prolonged activities that strain the body’s soft tissues, particularly in the upper limbs and back. This can occur in various settings, from offices where individuals type for extended periods to athletes engaging in repetitive sports movements. The condition is characterized by symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in affected areas.
Several factors contribute to RSI development. Poor posture during activities like typing or carrying heavy objects increases the risk. Ergonomic factors play a significant role; inadequate workstation setup, improper lifting techniques, and prolonged awkward positions can all lead to RSI. In some cases, pre-existing conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendinitis may worsen with repetitive actions. Additionally, mental health challenges such as stress and anxiety can exacerbate physical symptoms associated with RSI, creating a cycle of chronic pain and discomfort, prompting individuals to seek solutions for both the primary injury and potential underlying psychological factors, including considering treatment options like spinal adjustment, shockwave therapy for pain, or exploring strategies for chronic pain relief.
Psychological Impact of Chronic Pain and Discomfort
Chronic pain associated with repetitive strain injury (RSI) can take a significant toll on an individual’s mental health. The constant discomfort and limitations imposed by RSI often lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and even depression. Patients may struggle with a loss of independence and the ability to engage in activities they once enjoyed, which can result in reduced social interactions and a sense of disconnection from their support networks. This psychological impact is not to be underestimated; it can create a vicious cycle where pain intensifies due to heightened stress levels and negative thinking patterns.
Moreover, the journey towards recovery after an auto accident or any other injury that contributes to RSI can be emotionally challenging. Many individuals experience anxiety related to the prospect of returning to work or daily routines without exacerbating their symptoms. Therapeutic exercises designed for pain management and neck pain relief may offer some respite, but the mental health implications of chronic pain require equal attention. Effective treatment strategies should incorporate psychological support to address the emotional toll, fostering resilience and a sense of control over one’s recovery process.
Effective Coping Strategies for Mental Wellness
Dealing with Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) can take a significant toll on mental health due to its impact on daily activities and overall well-being. To combat this, adopting effective coping strategies is essential for maintaining mental wellness alongside physical recovery. One proven method is incorporating mindfulness practices like meditation or deep breathing exercises into one’s routine. These techniques help manage stress, improve focus, and foster a sense of calm, which can alleviate symptoms associated with anxiety and depression often linked to RSI.
Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity tailored to personal needs offers substantial mental health benefits. While avoiding strenuous activities that exacerbate RSI, low-impact exercises such as yoga or swimming can promote blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and boost endorphin levels. Tailored treatment plans, including personalized therapy sessions or support groups, empower individuals to share experiences, gain insights, and develop coping mechanisms specific to their unique challenges. Back pain relief and sports injury treatment may also be integrated into these strategies for a holistic approach to mental wellness during RSI recovery.
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) not only impacts physical health but significantly affects mental well-being. By understanding RSI’s causes, recognizing the psychological impact of chronic pain, and adopting effective coping strategies, individuals can navigate their mental health challenges associated with this condition. Prioritizing mental wellness is essential for a holistic approach to managing RSI, ensuring a better quality of life.